Before installing an operating system, you must understand these terms.
1️⃣ What is BIOS and UEFI?
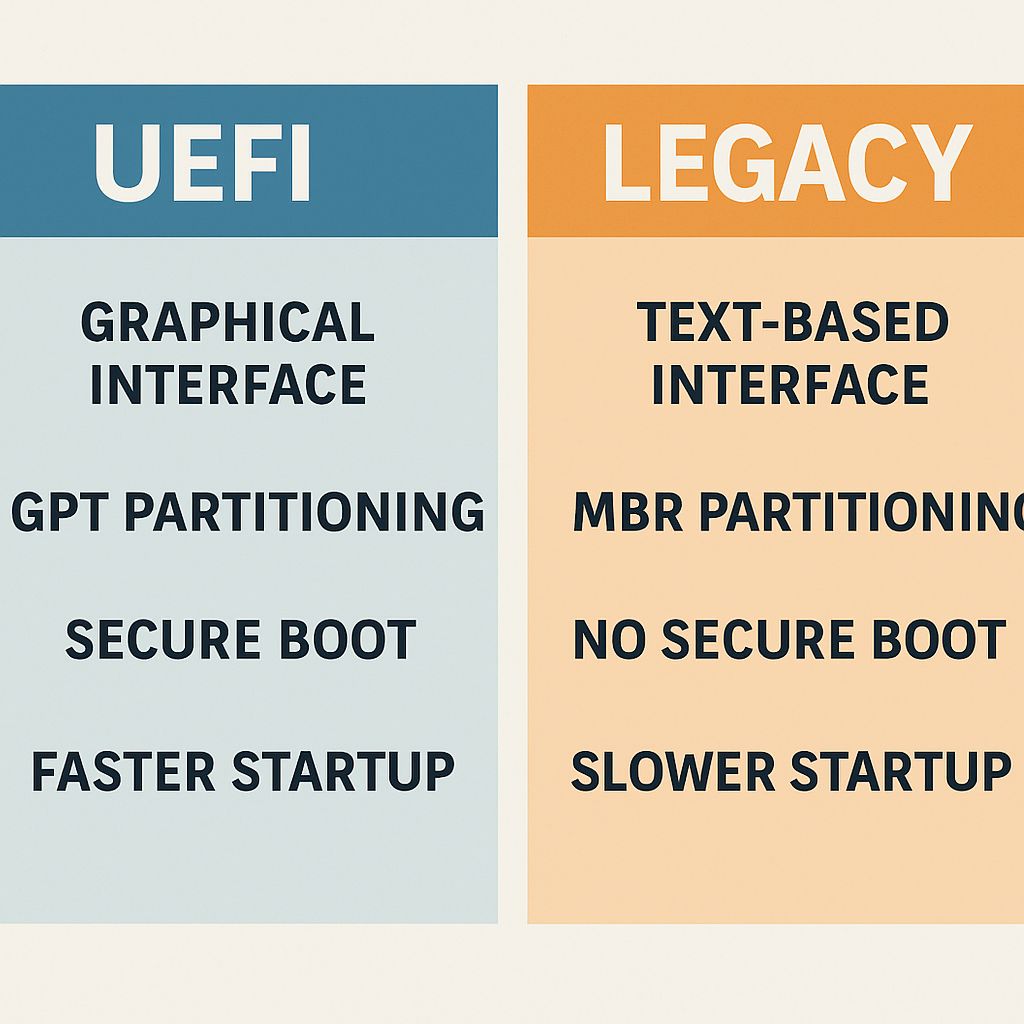
When you power on your PC, the first thing that runs is the firmware—either BIOS or the newer UEFI.
| Feature | BIOS (Legacy) | UEFI |
|---|---|---|
| Introduced | 1975+ | 2012+ |
| Disk Support | Up to 2 TB | Up to 9 ZB (Zettabytes) |
| Interface | Text-based | Graphical support |
| Boot Speed | Slower | Faster |
| Security | Minimal | Secure Boot & more |
Most modern systems come with UEFI. Legacy BIOS is found in older computers or in “Legacy Mode.”
2️⃣ What is MBR and GPT?
These are partitioning systems that define how your hard drive is structured and how data is stored.
| Feature | MBR (Master Boot Record) | GPT (GUID Partition Table) |
|---|---|---|
| Max Disk Size | 2 TB | 9 ZB |
| Partition Limit | 4 Primary Partitions | Up to 128 Partitions |
| Compatibility | Works with old systems | Designed for modern systems |
| Reliability | Basic | Includes redundancy headers |
3️⃣ Which One Should You Use?
If you’re using a modern PC:
- UEFI + GPT is highly recommended.
- It’s faster, safer, and supports larger drives.
On older PCs or for compatibility:
- Legacy + MBR may be required.
- Especially when installing older systems like Windows 7.
4️⃣ When Does It Matter?
- During USB preparation with Rufus, you must select the correct partition scheme and target system.
- If BIOS/UEFI settings are wrong, your drive might not appear during installation, or the OS won’t boot.
🧪 Example Scenario
Installing Windows 11 on a modern laptop?
- In Rufus: select
GPT + UEFI - In BIOS: enable
Secure Boot, disableLegacy Mode
🎯 Conclusion
| PC Type | BIOS Mode | Partition Scheme |
|---|---|---|
| Old PC (pre-2010) | Legacy | MBR |
| New PC (post-2012) | UEFI | GPT |
| Having issues? | Legacy | MBR |